There are many, many types of books in the world, which makes good sense, because there are many, many types of people, and everybody wants to read something different. —Lemony Snicke

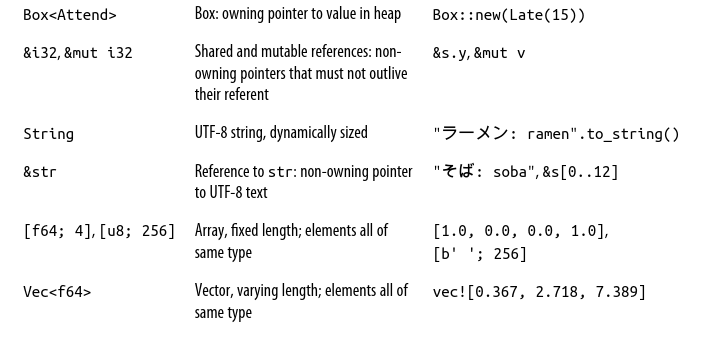
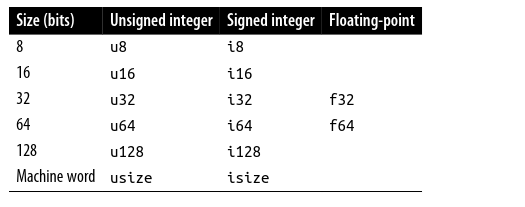
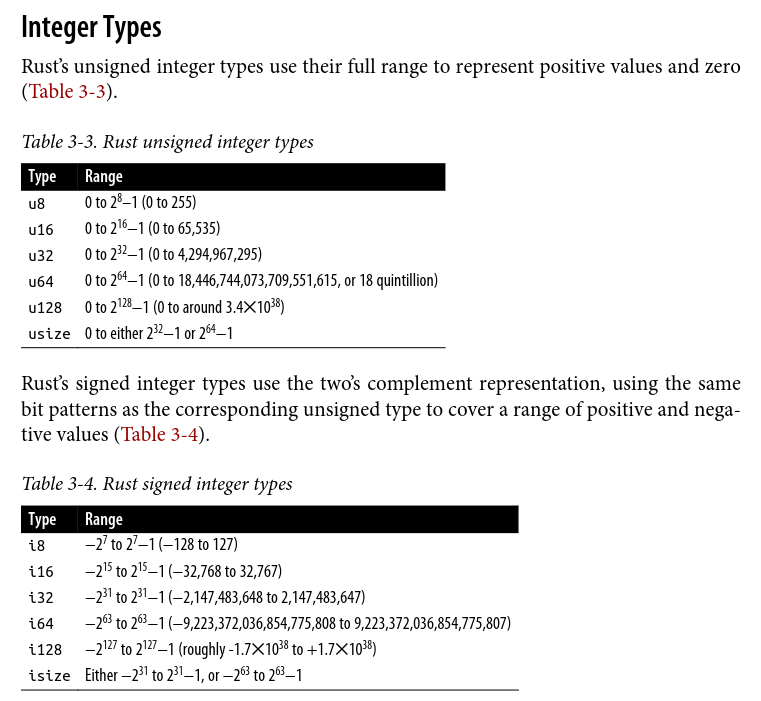
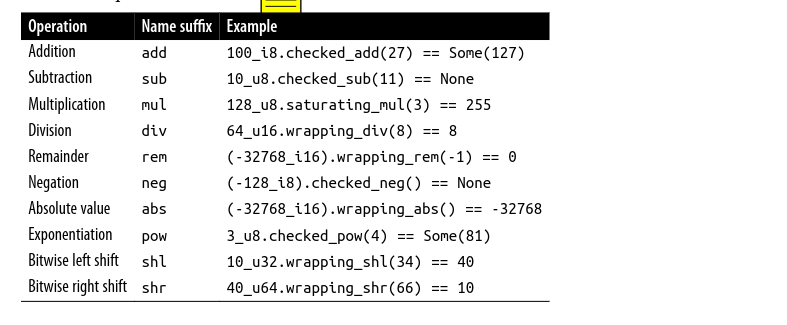
Fixed-Width Numeric Types
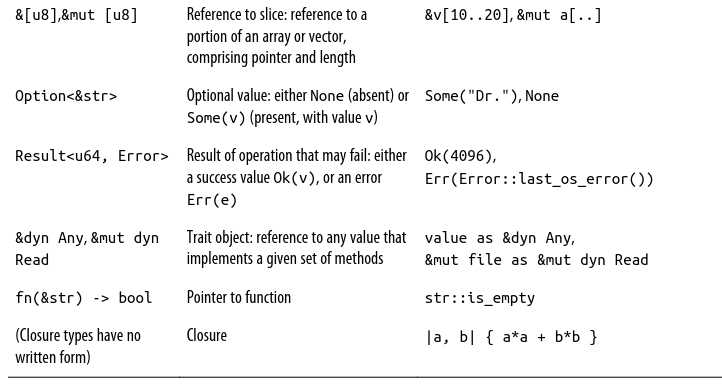
// 10_u8.checked_mul(10).expect("数值溢出");
// 100_u8.checked_add(200).expect("");
// let x = 100_u8;
// let y = 100_u8;
// // Do the addition; panic if it overflows.
// let sum = x.checked_add(y).unwrap();
// 超出不报错
500_u16.wrapping_mul(500); // 53392
500_i16.wrapping_mul(500); // -12144
// In bitwise shift operations, the shift distance
// is wrapped to fall within the size of the value.
// So a shift of 17 bits in a 16-bit type is a shift
// of 1.
// assert_eq!(5_i16.wrapping_shl(17), 10);
Characters
assert_eq!('*' as i32, 42);
assert_eq!('ಠ' as u16, 0xca0);
assert_eq!('ಠ' as i8, -0x60); // U+0CA0 truncated to eight bits, signedassert_eq!('*'.is_alphabetic(), false);
assert_eq!('β'.is_alphabetic(), true);
assert_eq!('8'.to_digit(10), Some(8));
assert_eq!('ಠ'.len_utf8(), 3);
assert_eq!(std::char::from_digit(2, 10), Some('2'));Tuples
let text = "I see the eigenvalue in thine eye";
let (head, tail) = text.split_at(21);
assert_eq!(head, "I see the eigenvalue ");
assert_eq!(tail, "in thine eye");let text = "I see the eigenvalue in thine eye";
let temp = text.split_at(21);
let head = temp.0;
let tail = temp.1;
assert_eq!(head, "I see the eigenvalue ");
assert_eq!(tail, "in thine eye");Slices
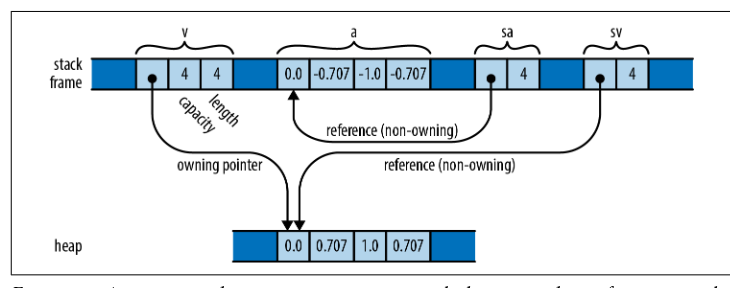
let v: Vec<f64> = vec![0.0, 0.707, 1.0, 0.707];
let a: [f64; 4] = [0.0, -0.707, -1.0, -0.707];
let sv: &[f64] = &v;
let sa: &[f64] = &a;Error: The variable `sv` contains a reference with a non-static lifetime so
can't be persisted. You can prevent this error by making sure that the
variable goes out of scope - i.e. wrapping the code in {}.
[E0597] Error: `a` does not live long enough
╭─[command_23:1:1]
│
2 │ let a: [f64; 4] = [0.0, -0.707, -1.0, -0.707];
│ ┬
│ ╰── binding `a` declared here
│
4 │ let sa: &[f64] = &a;
│ ─┬
│ ╰── borrowed value does not live long enough
│ │
│ ╰── cast requires that `a` is borrowed for `'static`
───╯
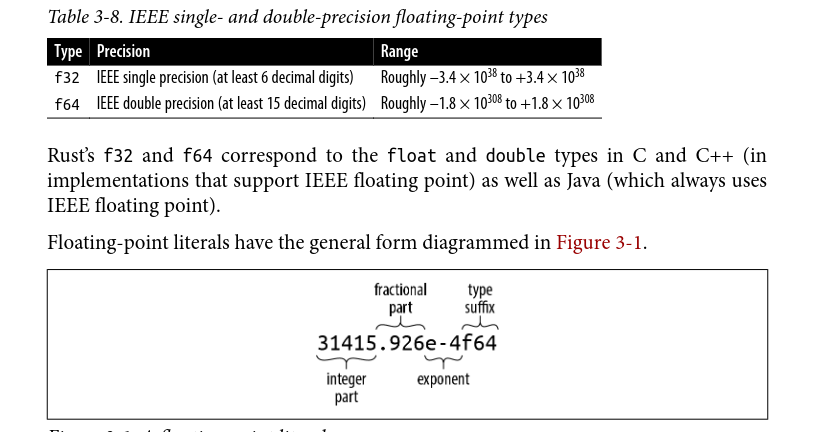
String Literals
println!("In the room the women come and go,
Singing of Mount Abora");
println!("It was a bright, cold day in April, and \
there were four of us—\
more or less.");
let default_win_install_path = r"C:\Program Files\Gorillas";
println!(r###"
This raw string started with 'r###"'.
Therefore it does not end until we reach a quote mark ('"')
followed immediately by three pound signs ('###'):
"###);
In the room the women come and go,
Singing of Mount Abora
It was a bright, cold day in April, and there were four of us—more or less.
This raw string started with 'r###"'.
Therefore it does not end until we reach a quote mark ('"')
followed immediately by three pound signs ('###'):Byte Strings
let method = b"GET";
assert_eq!(method, &[b'G', b'E', b'T']);
Strings
let noodles = "noodles".to_string();
let oodles = &noodles[1..];
let poodles = "ಠ_ಠ";let oodles = &noodles[1..];
let oodles = &noodles[1..];
^^^^^^
The variable `oodles` contains a reference with a non-static lifetime so
can't be persisted. You can prevent this error by making sure that the
variable goes out of scope - i.e. wrapping the code in {}.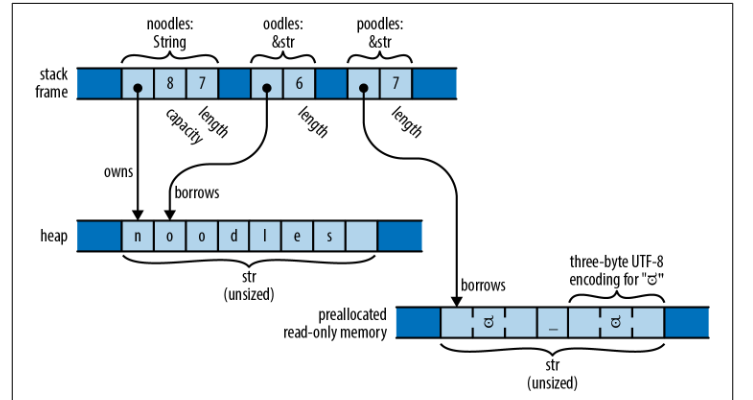
assert_eq!("ಠ_ಠ".len(), 7);
assert_eq!("ಠ_ಠ".chars().count(), 3)()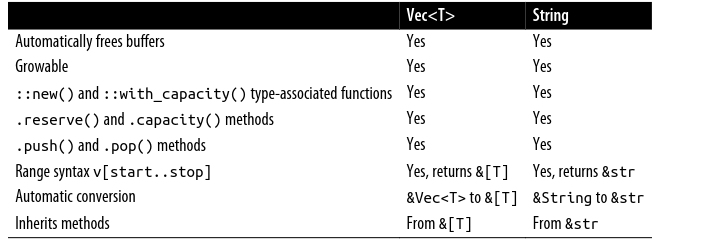
let error_message = "too many pets".to_string();println!("{}",error_message)too many pets
()format string
println!("{}",format!("{}°{:02}′{:02}″N", 24, 5, 23))24°05′23″N
()let bits = vec!["veni", "vidi", "vici"];bits.concat()"venividivici"bits.join(",")"veni,vidi,vici""ONE".to_lowercase()"one""peanut".contains("nut")true"ಠ_ಠ".replace("ಠ", "■")"■_■"